What is an archival control model?
An archival control model (ACM) is a data model, metadata scheme and intellectual framework for documenting archival records and the agencies that created and managed the records. It provides a structured and systematic approach to describing records and their context so their original purpose is self-evident and their value as evidence of government administration is preserved.
Archivists use ACMs as the basis for their archival systems and catalogues, helping users to locate, access and understand records both within and external to the physical collection.
It is underpinned by the archival principles of respect for original order and provenance (respect des fonds).
PROV ACM
|
See the:
|
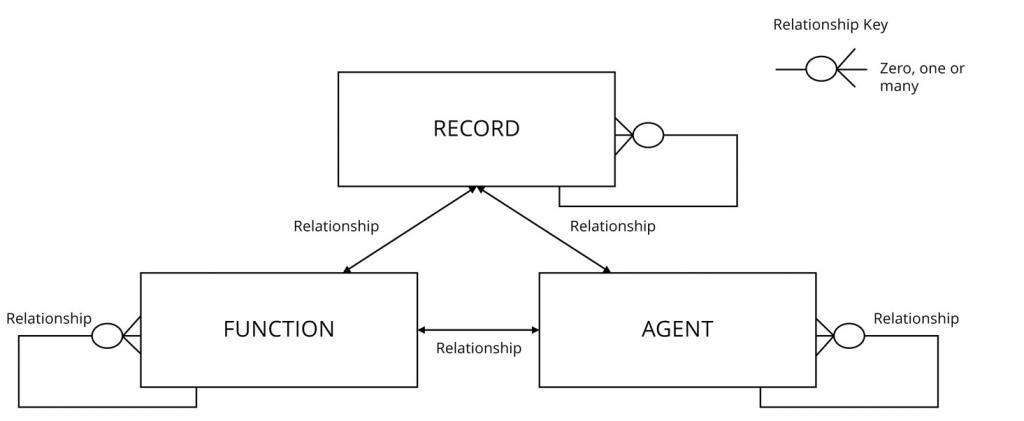
The PROV ACM describes both entities and the relationships between entities. The three main entities of the ACM are: Record, Function and Agent.
The ACM:
- has a simple and flexible structure, not hierarchical
- represents all records consistently, irrespective of whether they are digital or physical
- conforms to existing systems and standards including:
- Australian Series System
- AS/NZ 5478 Recordkeeping Metadata Property Reference Set
- Records in Contexts (RiC) Standard for Archival Description.
Record entity
AS/NZ 5478 definition: A record, is information in any format created, received and maintained as evidence by an organisation or person, in pursuant of legal obligations or in the transaction of business. A record may comprise of electronic or paper-based document or group of aggregated documents.
The record entity in PROV’s ACM represents ‘public records’ as defined in the Public Records Act 1973.
In the ACM, there are two subtypes of the Record entity:
- Record Series: a group of records which are recorded or maintained by the same agency (or agencies) and which:
- are in the same numerical, alphabetical, chronological or other identifiable sequence; or
- result from the same accumulation or filing process.
- Record Item: a discrete element records managed within a ‘Series’. An Item represents a part of a recordkeeping system or a logical or convenient grouping of records. It may represent one record or multiple records such as a group of folios fastened together to form a file, a group of electronic files aggregated in a folder, or a single volume.
Function entity
AS/NZ 5478 definition: Functions are major responsibilities managed by an organisation to fulfil its goals and high-level aggregates of an organisation’s activities.
The function entity in PROV’s ACM represents the major responsibilities of Victorian Government that may be managed by one or more agencies over time. Applying this entity helps to:
- group together various records with the same administrative record context
- links records to their provenance and complementary information.
Agent entity
AS/NZ 5478 definition: An agent is a corporate entity, organisational property or system, or individual responsible for the performance of some business activity, including actions on records.
The agent entity in PROV’s ACM represents a Victorian Government agency—an administrative unit which has or had responsibility for the provision of at least one aspect of government administration. This entity helps to provide a description of a record’s context, namely who created the records and for what purpose.